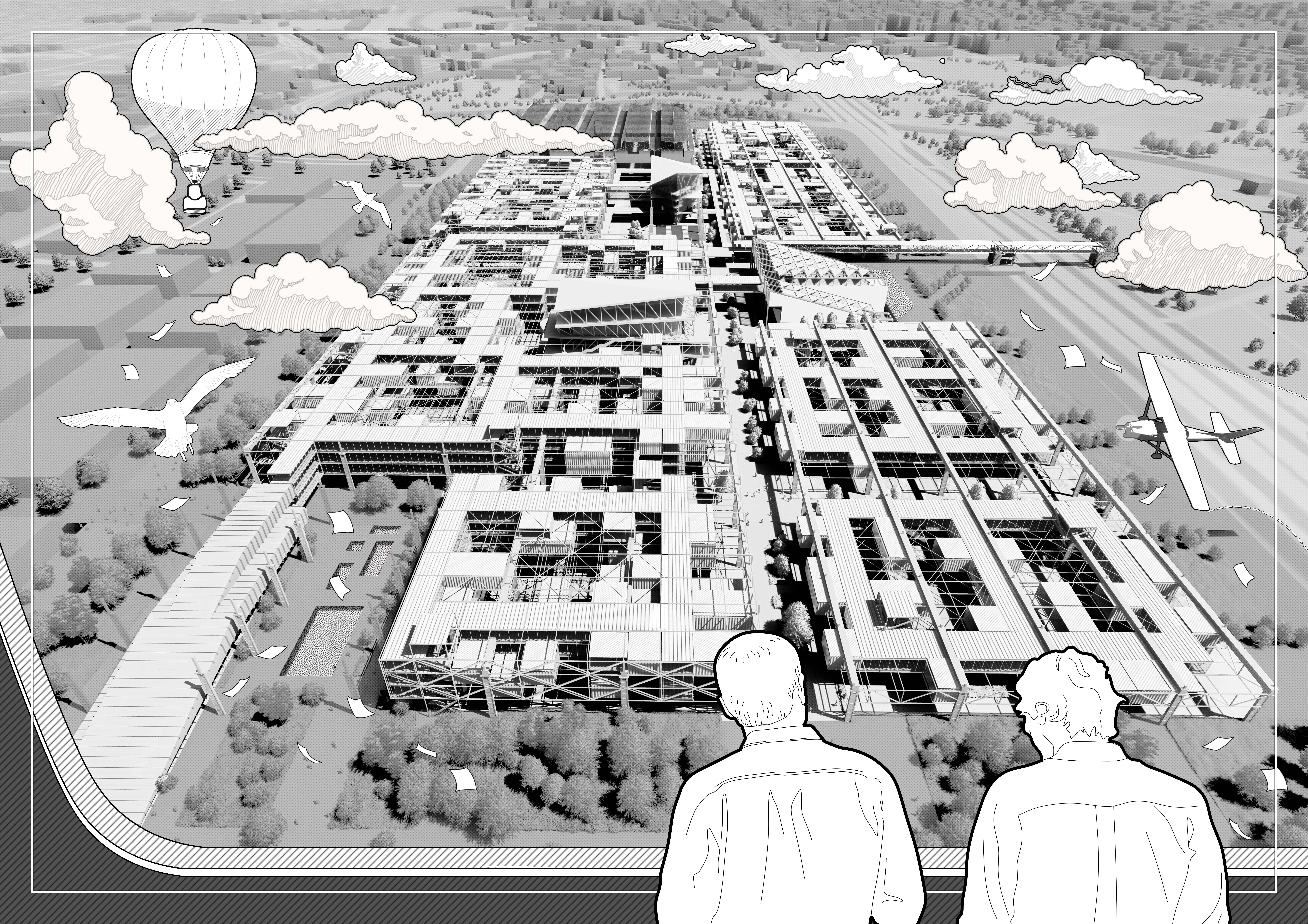
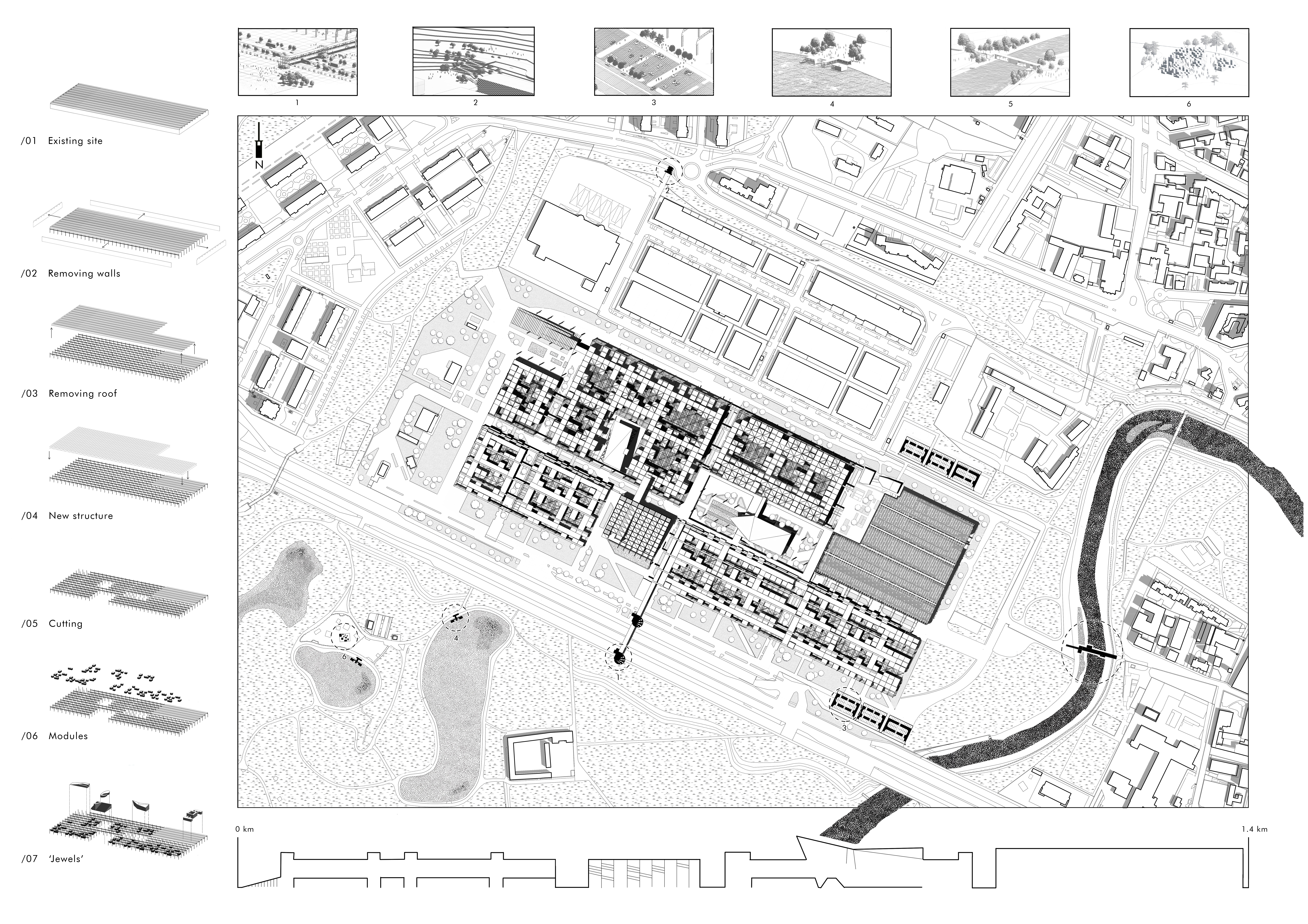
Located at the former ThyssenKrupp industrial site in Turin, this project addresses the complex challenges of post-industrial transformation in Europe's former manufacturing centers. The Exthyssenkrupp Factory project explores how obsolete industrial infrastructure can be regenerated as productive landscapes for contemporary urban life.
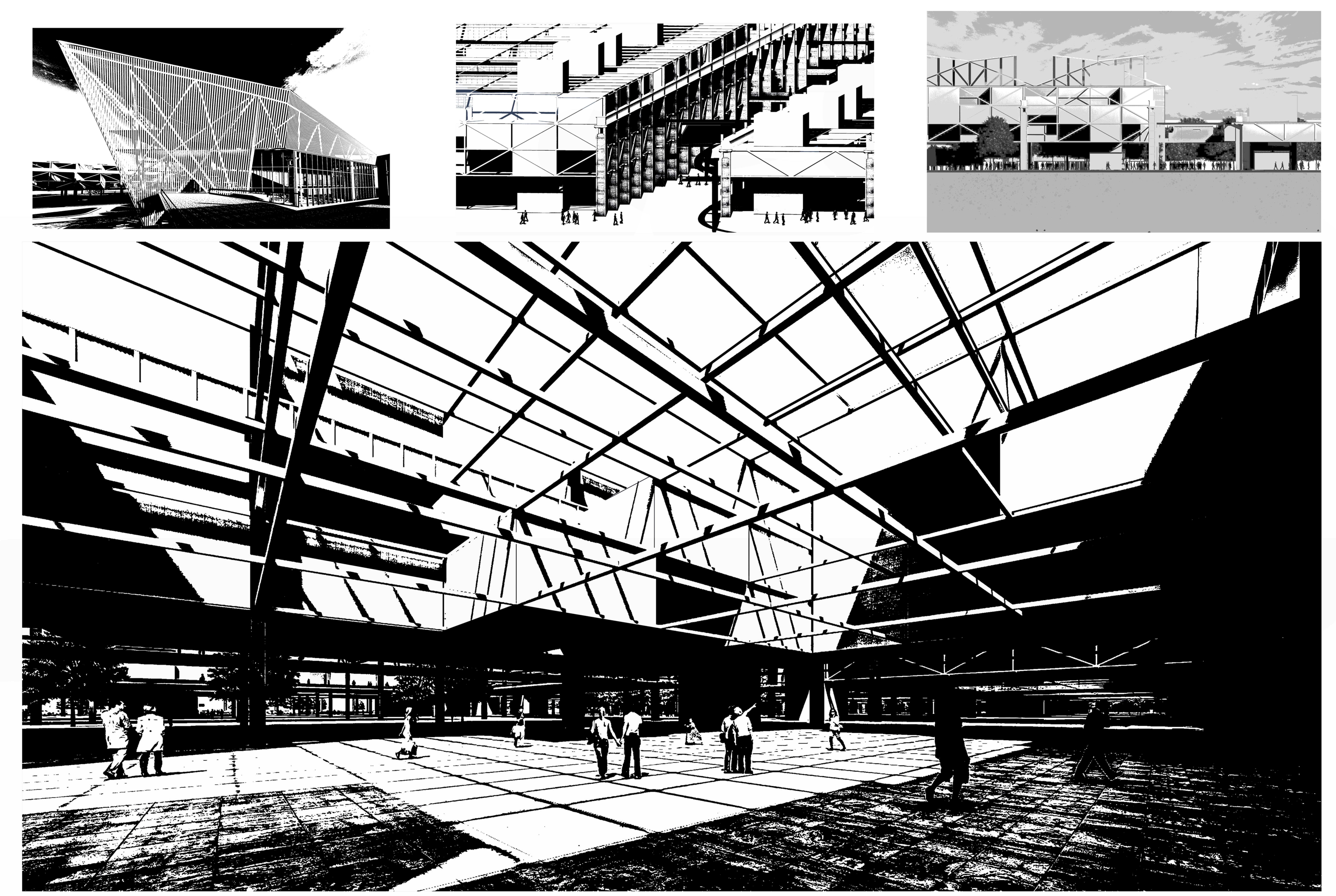
Rather than complete demolition, the design strategy selectively preserves significant industrial structures while introducing new programs that respond to current urban needs. This approach maintains historical continuity while enabling functional transformation.
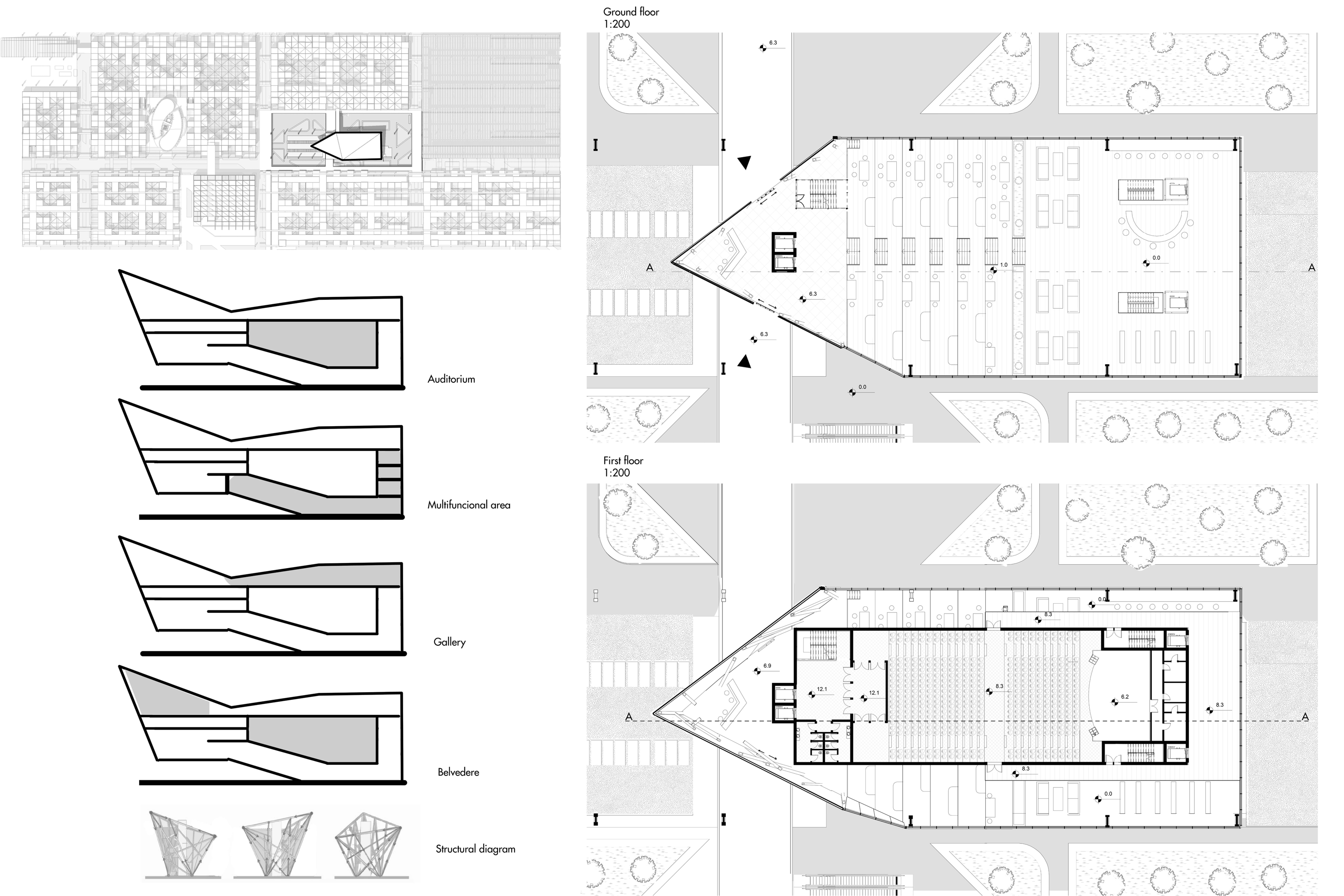
The regenerated complex combines residential, commercial, cultural, and light industrial uses within the existing building envelope. This programmatic diversity creates an active urban district that operates throughout the day and supports various community needs.
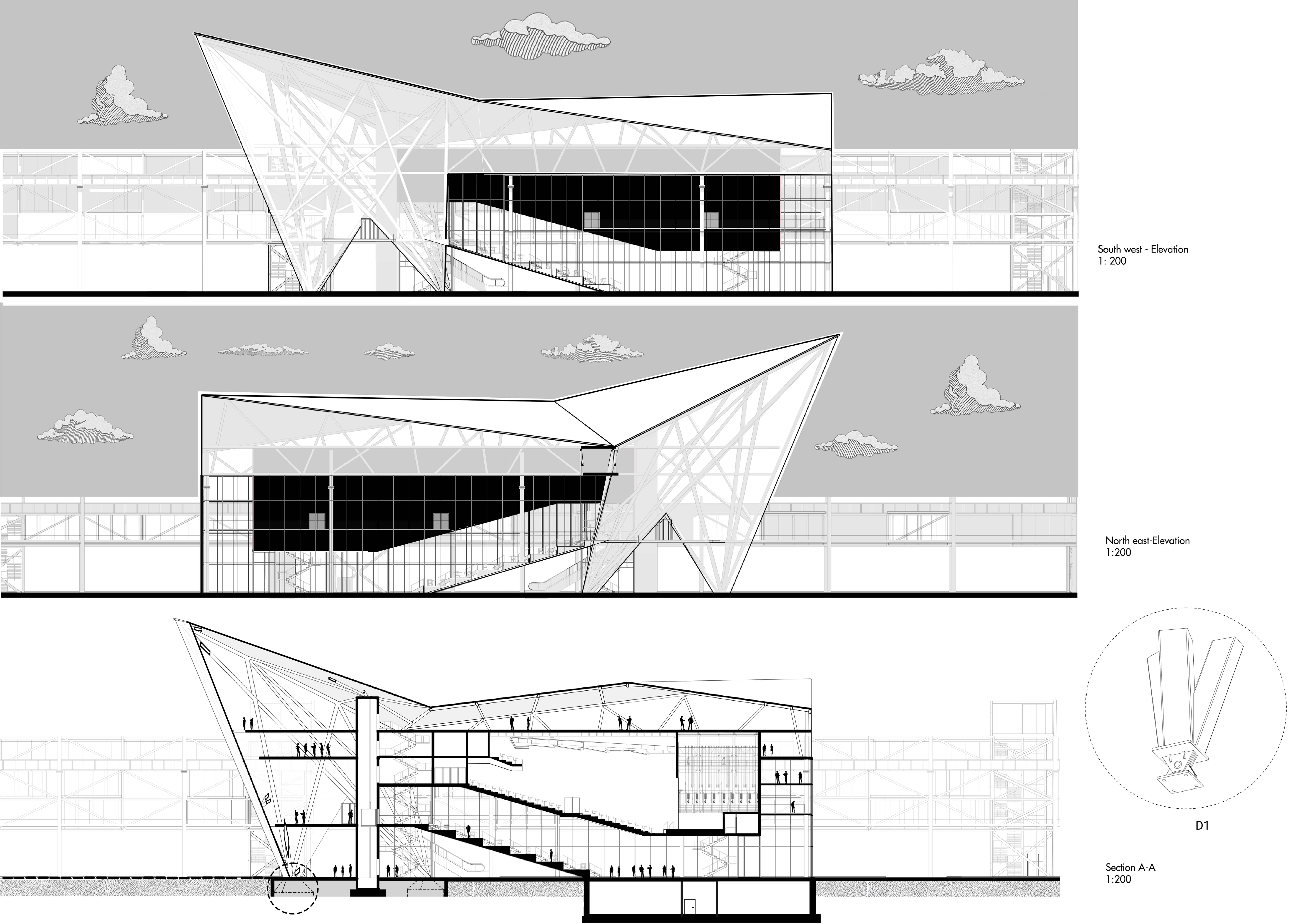
Environmental restoration is central to the project, with contaminated soils being treated through bioremediation processes while new landscape systems improve air quality and stormwater management. The site becomes a model for ecological regeneration in post-industrial contexts.
The project creates new economic opportunities through maker spaces, startup incubators, and creative industries that build on Turin's manufacturing heritage while embracing digital and sustainable technologies. This economic diversification supports long-term urban resilience.